4.3.1 Overview of local boards
Local boards were introduced on 1 November 2010 as part of Auckland’s local governance reforms. This was a new approach to local government in New Zealand.
The government described the local board and governing body model as:
“A new and different form of local governance and the parties have been empowered to work together to ensure that an effective and appropriate balance is reached between regional and local interests” [1]
Purpose of local boards
Local boards have a significant and wide-ranging role that spans many council services and activities. They:
- make decisions on local matters
- provide local leadership
- help enable strong, connected communities.
They also:
- support democratic decision-making by, and on behalf of, local communities
- help meet the purpose of local government [2], by ensuring all communities in the Auckland region are represented by one of the 21 local boards.
Local board membership
There are 21 local boards across Auckland. These vary in population size — from Howick (153,570 people at the last census) to Great Barrier (1251 people).
How boards were set up
Before Auckland Council was formed, the Local Government Commission determined:
- the number of local boards
- their geographic boundaries
- the number of elected members per board.
This was done under the Local Government (Auckland Council) Act 2009.
Local board members:
- can only serve on one board
- can stand for more than one board but must state their preferred choice in their election candidate profile statement [3].
Each board elects (from among its members):
- a chair
- a deputy chair.
Subdivisions
Some local boards are divided into subdivisions. For example:
- Franklin Local Board has three subdivisions, covering an area from Waiuku (west coast) to Maraetai (east coast).
- Members elected from each subdivision make up the full Franklin Local Board and make decisions for the whole board area.
Members should act in the interests of the entire board area, not just their subdivision.
Current board makeup
| Local Board Areas | Subdivisions (if they exist) | Number of members |
|
Albert-Eden |
Ōwairaka |
4 |
|
|
Maungawhau |
4 |
|
Devonport-Takapuna |
|
6 |
|
Franklin |
Pukekohe |
4 |
|
|
Wairoa |
3 |
|
|
Waiuku |
2 |
|
Āotea/Great Barrier |
|
5 |
|
Henderson-Massey |
|
8 |
|
Hibiscus and Bays |
East Coast Bays |
4 |
|
|
Hibiscus Coast |
4 |
|
Howick |
Botany |
3 |
|
|
Howick |
3 |
|
|
Pakuranga |
3 |
|
Kaipātiki |
|
8 |
|
Mangere-Otahuhu |
|
7 |
|
Manurewa |
|
8 |
|
Maungakiekie-Tāmaki |
Maungakiekie |
3 |
|
|
Tāmaki |
4 |
|
Ōrakei |
|
7 |
|
Ōtara-Papatoetoe |
Ōtara |
3 |
|
|
Papatoetoe |
4 |
|
Papakura |
|
6 |
|
Puketāpapa |
|
6 |
|
Rodney |
Dairy Flat |
1 |
|
|
Kumeu |
4 |
|
|
Warkworth |
3 |
|
|
Wellsford |
1 |
|
Upper Harbour |
|
6 |
|
Waiheke |
|
5 |
|
Waitakere Ranges |
|
6 |
|
Waitematā |
|
7 |
|
Whau |
|
7 |
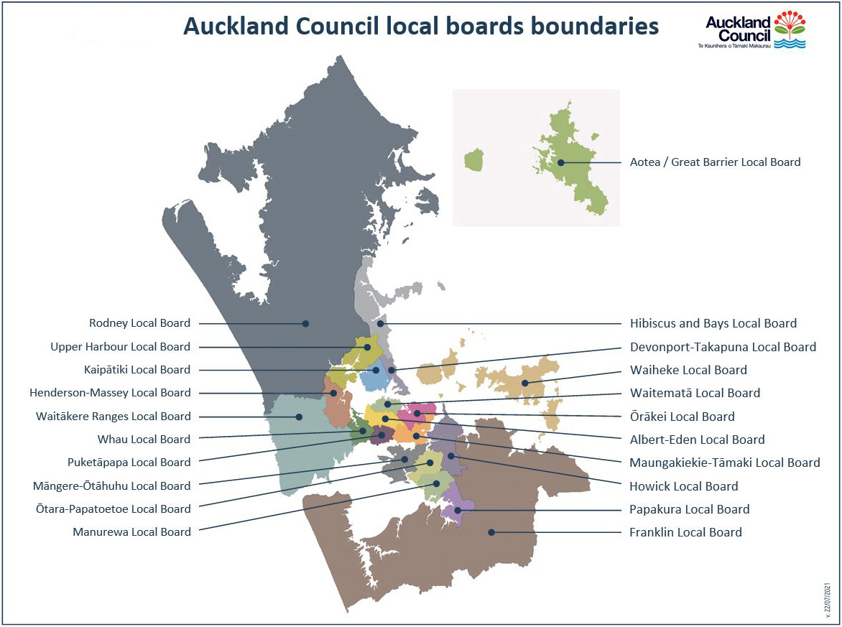
To learn more, visit Local boards.
For details about the role of local board members, visit Local board responsibilities.
Representation reviews
Auckland Council must review local board representation at least once every six years [4].
This review can:
- recommend changes to the number of members on a local board (between five and 12 allowed under law)
- respond to changes in population and community needs.
The review cannot change local board boundaries apart from minor changes. That can only happen through:
- a local government reorganisation proposal
- a change to legislation [5].
- Legal status of local boards (h2)
- Local boards are:
- part of Auckland Council
- not local authorities in their own right, but rather incorporated bodies
- not community boards or governing body committees.
Legal powers and limits
Local boards cannot (in their own right):
- buy, hold or sell property
- enter into contracts
- employ or dismiss staff
- be a party to legal proceedings [6].
Although not a local authority, the legal requirements around decision-making in the Local Government Act 2002 apply to local boards as if they are a local authority. In practice, when making decisions, this means that local boards will take all steps that a local authority would take.
Footnotes
[1] Cabinet paper (Nov 2009) “Local Government (Auckland Law Reform) Bill: Planning, Reporting, Rates and Local Boards”, on the Department of Internal Affairs website.
[2] Local Government (Auckland Council) Act 2009 section 10.
[3] Local Government (Auckland Council) Act 2002 sections 11AA, 11AAB.
[4] Local Government (Auckland Council) Act 2009 section 103 and Local Electoral Act 2001 section 19H.
[5] Section 11 Local Government (Auckland Council) Act
[6] Local Government (Auckland Council) Act 2009 section 12.